This post is also available in: Persian Armenian
The oil industry is one of the most complex and critical industries in the world, playing a vital role in energy supply and the global economy. With increasing environmental pressures, global competition, and the need for process optimization, the adoption of advanced technologies to enhance safety, productivity, and sustainability has become essential. Among these technologies, nitrogen gas (N₂), with its unique properties, has gained a significant role in key processes within the oil industry.
Nitrogen, with features such as chemical inertness, non-flammability, dryness, and high availability, plays a crucial role in various operations such as injection into reservoirs, corrosion prevention, pipeline testing, equipment cleaning, system safety, and drilling support. This article explores the comprehensive applications, benefits, limitations, and safety considerations related to nitrogen use in the oil industry.
Physical and Chemical Properties of Nitrogen Gas
Nitrogen is one of the primary components of the Earth’s atmosphere (approximately 78% by volume). The following physical and chemical properties make it highly suitable for sensitive applications in the oil industry:
- Inertness: High reactivity due to the strong triple bond between two nitrogen atoms.
- Non-flammability: In hydrocarbon-rich environments, using non-flammable gases like nitrogen is essential.
- Dryness: Dry nitrogen reduces moisture in equipment, preventing corrosion.
- Compressibility & Storage: Nitrogen can be transported and stored at high pressures in oil fields.
- On-site Production: Nitrogen can be produced locally using PSA (Pressure Swing Adsorption) or membrane systems, eliminating the need for constant external supply.
Nitrogen Injection for Reservoir Pressure Maintenance
During the secondary recovery phase of oil extraction, after the natural pressure in the reservoir decreases, gas injection is used to continue production. Nitrogen is one of the safest and most cost-effective options compared to other gases like CO₂ and H₂S.
How It Works:
- Nitrogen is injected into the upper part of the reservoir, creating pressure that facilitates the flow of oil towards the production well.
- In high-temperature, deep oil fields, nitrogen maintains its stability and exhibits minimal reactivity.
Benefits:
- Reduces the formation of undesirable chemical compounds.
- Increases recovery factor (RF).
- High safety compared to corrosive or flammable gases.
- Reduces the need for chemical additives for corrosion control.
Corrosion Mitigation in Equipment and Pipelines
Corrosion is one of the most costly challenges in the oil industry, leading to equipment degradation, leaks, and increased risk of accidents. Nitrogen plays an essential role in preventing corrosion in systems with oxygen or water vapor.
Key Applications:
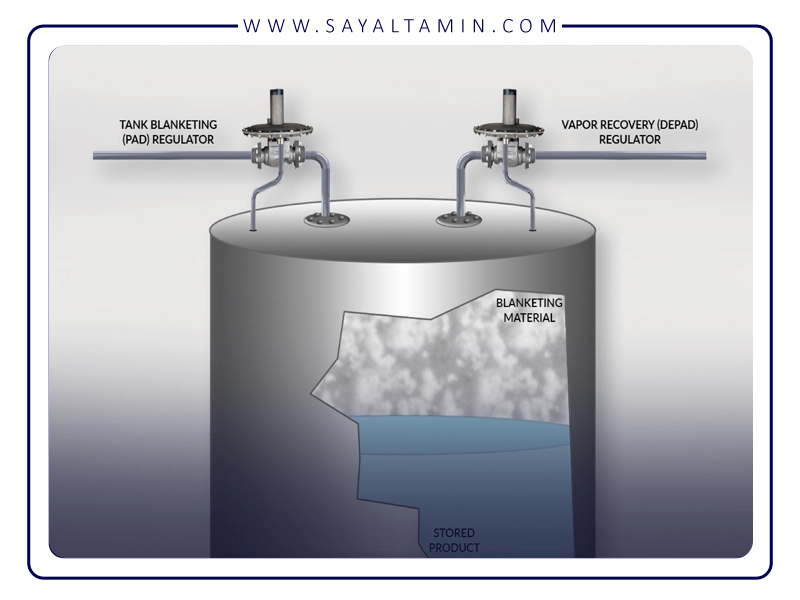
- Blanketing storage tanks: Injecting nitrogen into the headspace above stored liquids removes oxygen and moisture, reducing the risk of oxidation and corrosion.
- Preventing internal corrosion in pipelines: During downtime or maintenance, filling the internal space of pipelines with nitrogen prevents corrosive materials from contacting metal surfaces.
- Creating an inert atmosphere in reactors and refineries: Particularly in processes dealing with volatile or flammable compounds.
Benefits:
- Extends the life of storage tanks, heat exchangers, boilers, and pipelines.
- Reduces maintenance costs and repair frequency.
- Minimizes corrosion rates in acidic or saline environments.
Pipeline Pressure Testing & Cleaning

Before using oil or gas transmission pipelines, pressure testing and cleaning must be performed to ensure safety and performance.
Nitrogen Pressure Testing:
In cases where water cannot be used (e.g., in cold regions or sensitive pipelines), compressed nitrogen serves as a suitable alternative.
Pipeline Cleaning (Pigging & Purging):
- After a pigging operation, nitrogen is used to drain and fully dry the pipeline.
- This process helps reduce the risk of explosions, corrosion, and contamination.
Benefits:
- Higher safety compared to compressed air or other gases.
- Prevents freezing or blockages in low-temperature conditions.
- Prepares pipelines for material transfer without the need for hazardous chemicals.
Drilling & Completion Support
During drilling operations, well pressure control and preventing the influx of gas or fluids into the well are crucial. Nitrogen plays several roles in this phase:
- Used in underbalanced drilling fluids.
- Provides pressure control during well completion.
- Helps clean the well and evacuate excess fluids.
| Read more: Application of liquid oxygen in the refining and oil industry |
Additional Applications in Processes & Maintenance:
- Nitrogen Flooding: An advanced method for injecting nitrogen to displace heavy oil in reservoirs.
- Equipment Preservation: Nitrogen is used to prevent rusting of sensitive components during storage.
- Cryogenic Equipment Cooling: In specific cryogenic processes.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Using Nitrogen in the Oil Industry

Benefits:
- High Safety: No explosion, combustion, or reaction with hydrocarbons.
- Reduced Corrosion Rates: Long-term protection of critical equipment.
- Cost-Effective: On-site nitrogen production reduces reliance on external supply chains.
- Environmentally Friendly: No direct greenhouse effect and no toxic residue.
Drawbacks:
- Asphyxiation Risk: In confined spaces with poor ventilation, replacing oxygen with nitrogen can be lethal.
- Special Equipment Required: For transporting, storing, and injecting nitrogen under pressure or in liquid form.
- Cryogenic Burns: In liquid form, nitrogen can cause severe skin burns.
Safety Requirements & International Standards
Given the potential hazards, adherence to international standards is essential.
Key Regulations:
- Adequate ventilation in confined spaces.
- Installation of Oxygen (O₂) monitors.
- Full staff training on nitrogen hazards.
- Use of Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): including cold-resistant gloves, masks, safety boots, and specialized clothing.
- Regular inspection of equipment and connections.
- Proper labeling of tanks and pipelines.
Reference Standards:ISO 14118
OSHA 1910
NFPA 55
API 521
| Read more: Application of liquid carbon dioxide in the oil industry |
Due to its unique chemical properties and high safety, nitrogen is a key and strategic component in various operations across the oil industry. Its wide range of applications—from reservoir injection to system cleaning and corrosion mitigation—enhances efficiency, reduces operational costs, and improves safety levels.
Companies involved in gas supply and oilfield services can create significant value for their clients by developing nitrogen infrastructure (including on-site production, safe injection systems, and advanced monitoring), thereby strengthening their position in the competitive market.
————————————————–
References
MinnuoGas: Applications of Nitrogen in Oil Fields




