This post is also available in: Persian Armenian
Nitrous oxide (N₂O), commonly known as “laughing gas,” is one of the most recognized and widely used inert gases in medical science. Due to its unique properties—such as anxiolytic effects, mild analgesia, and high safety—it has become a key tool in dental treatments, emergency care, childbirth, pediatric procedures, and even psychiatric therapies. Unlike general anesthesia or oral sedatives, nitrous oxide offers precise controllability, rapid onset, and immediate recovery, making it one of the best options for pain relief and anxiety reduction.
History and Discovery
Nitrous oxide was discovered in the early 18th century by English chemist Joseph Priestley. Initially, it was used as an inert, odorless gas for non-medical and recreational purposes. Gradually, its calming and analgesic effects drew attention. Subsequently, dentists and physicians recognized that nitrous oxide could reduce patient anxiety and relieve pain, leading to its therapeutic applications. By the 19th century, its popularity as a short-acting, controllable anesthetic grew steadily, and today it holds a prominent position in medical and dental practice.
| Read more: Application of argon in medicine |
Physical and Chemical Properties
Nitrous oxide is a chemical compound with the formula N₂O. It is a colorless gas with a slightly sweet odor and lacks irritant properties. At room temperature, it remains gaseous but is stored as a liquid under pressure in cylinders. It is soluble in both water and lipids, which allows rapid absorption through the lungs and elimination unchanged via the same route.
Properties such as lack of hepatic or renal metabolism, absence of deep anesthesia induction, and minimal impact on blood pressure at therapeutic doses make N₂O one of the safest sedative agents for outpatient treatments.
Mechanism of Action

Nitrous oxide exerts its effects primarily via:
- GABA receptors activation: Reduces neuronal activity, leading to decreased anxiety and fear.
- NMDA receptor inhibition: Increases pain tolerance by reducing glutamate-mediated pain signaling.
Unlike general anesthetics, N₂O does not induce complete loss of consciousness. Instead, the patient remains calm, cooperative, and responsive throughout the procedure.
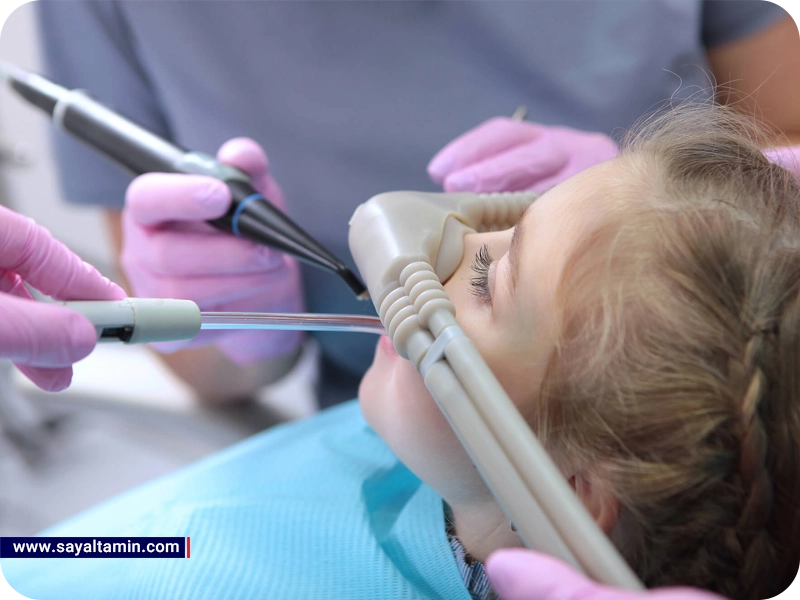
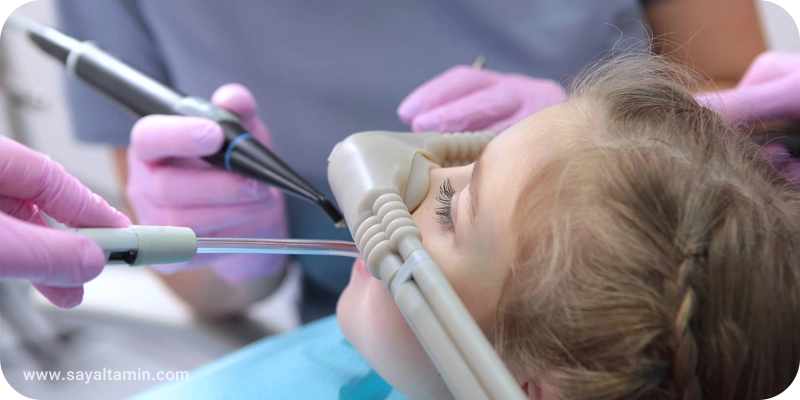
Applications in Dentistry
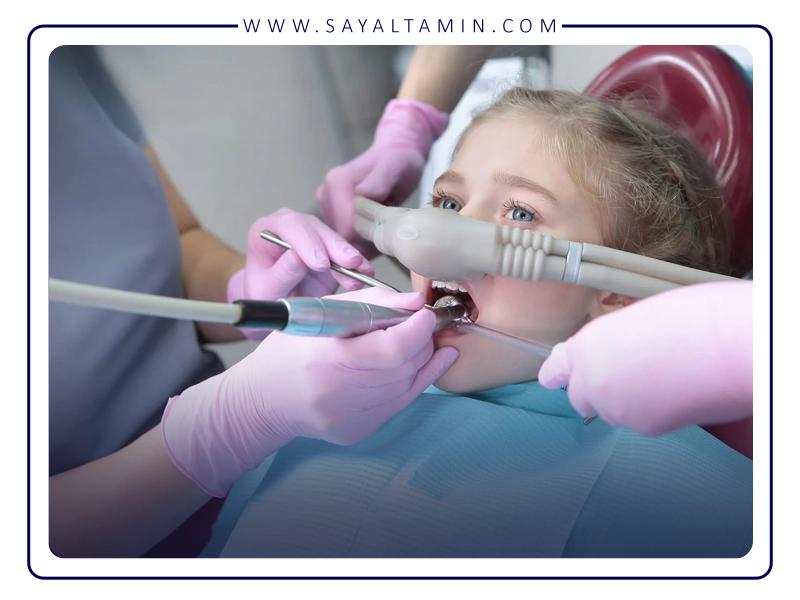
In dentistry, nitrous oxide is a rapid, safe, and effective sedative for reducing patient anxiety and pain. It plays a crucial role in improving patient experience during various procedures. Key dental applications include:
- Anxiety and Fear Reduction
Many patients—especially children, individuals with severe dental phobia, or those with prior negative experiences—experience stress and anxiety during dental treatments. Such anxiety can interfere with necessary procedures and trigger physiological responses like increased heart rate, elevated blood pressure, and rapid breathing. N₂O acts on the central nervous system to induce a sense of calm, significantly reducing anxiety. Its effects are immediately reversible and can be adjusted at any time during treatment.
- Pain management
Alongside local anesthesia, nitrous oxide provides mild, rapid-acting analgesia. It allows patients to experience less discomfort during procedures, which is particularly valuable in emergency treatments or for pain-sensitive individuals. Furthermore, it reduces reliance on stronger injectable medications, making treatments safer and more comfortable.
- Facilitation of Complex Procedures
For children, anxious patients, or those with extreme fear, nitrous oxide can simplify dental procedures, including minor surgeries, orthodontic adjustments, wisdom tooth extractions, or root canal treatments. In lengthy treatments, N₂O prolongs the duration of pain-free cooperation, enabling stress-free and efficient care.
- Minimizing Side Effects and Enhancing Patient Experience
Compared to injectable sedatives and stronger medications, nitrous oxide has fewer side effects and short duration of action. Patients recover immediately after administration, with minimal nausea or excessive drowsiness, making it the preferred option for pain and anxiety management in dentistry.
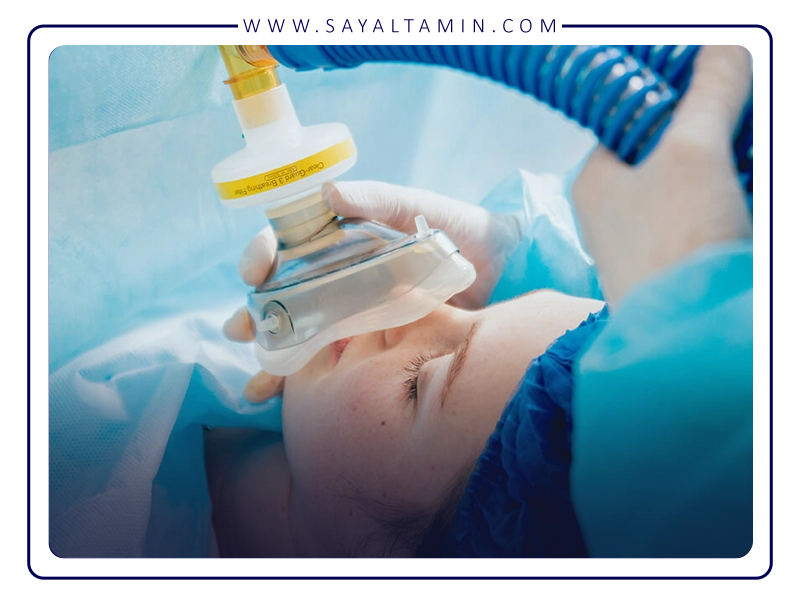
General medical and hospital applications
Emergency Care
In emergency departments, N₂O plays a vital role in rapid pain management for procedures such as wound dressing, suturing, fracture reduction, and other minor painful interventions.
Childbirth
In many countries, including Canada, Sweden, Finland, and New Zealand, nitrous oxide serves as a safe alternative to epidural analgesia during natural childbirth, allowing mothers to self-administer the gas under controlled conditions.
Pediatrics
Nitrous oxide is used to facilitate injections, vaccinations, suturing, MRI scans, and other minimally invasive procedures, keeping children calm without the need for full anesthesia.
Psychiatric Treatments
Recent studies have explored N₂O in treating treatment-resistant depression, severe anxiety disorders, and PTSD. Its short-acting sedative effect with minimal serious side effects makes it a promising therapeutic option.
| Read more: Medical oxygen in diving |
Comparison with other methods
| Nitrous Oxide | Oral Drugs | General Anesthesia | Features |
| Very fast | Slow (30 minutes) | Very fast | Speed of onset of action |
| Yes | No | Yes | Controlled by a doctor in real time |
| Within 5–10 minutes | Several hours | Long (recovery) | Full return to consciousness |
| Medium | Low | Very High | Requires specialized equipment |
| Medium | Low | Very High | Requires specialized equipment |
Safety, training and standards
Nitrous oxide is one of the safest options for pain and anxiety relief when used correctly. However, there are some things to keep in mind:
- Specialized training of doctors and staff
Proper ventilation of the treatment room
Safety, Training, and Standards
When used properly, nitrous oxide is one of the safest options for pain and anxiety management. However, adherence to certain precautions is essential:
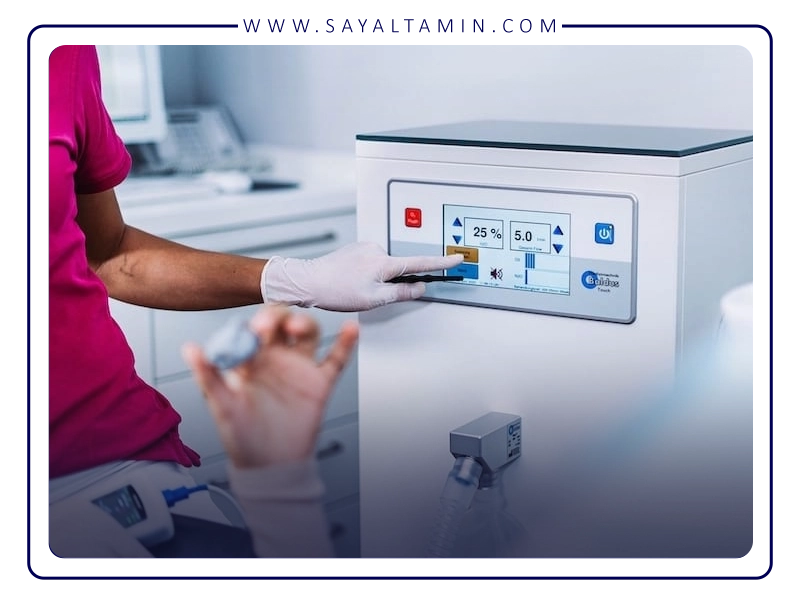

- Specialized training for physicians and staff
- Adequate ventilation in the treatment room and use of gas scavenging systems
- Review of patient history, including respiratory, cardiac, and neurological conditions
- Use of standardized masks to prevent gas leakage
Clinical Research and Future Directions
Published studies in the Journal of Dental Anesthesia indicate that:
- Pediatric patients demonstrated better cooperation in 85% of cases when N₂O was used.
- Recovery time after treatment was reported to be only 5 to 8 minutes.
- Over 90% of dentists reported high patient satisfaction following procedures with N₂O.
Ongoing research is exploring the role of nitrous oxide in psychiatric treatments, improving quality of life for specific patient groups, and developing intelligent devices for more precise gas administration.
Nitrous oxide is recognized as one of the safest, most effective, and rapid-acting sedative agents in medicine and dentistry. By providing a controlled, reversible, and safe environment, it has transformed the treatment experience for millions of patients worldwide. Specialized training, proper equipment, and strict adherence to safety protocols are essential for the successful utilization of this valuable tool.
————————————————–
References