This post is also available in: Persian Armenian
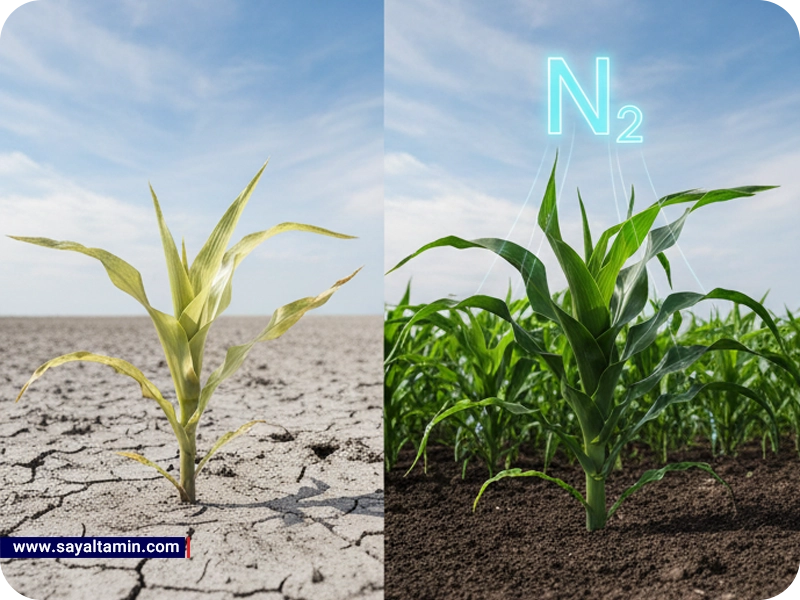
Nitrogen is an essential element for plant growth and development. It is a major component of amino acids, proteins, nucleic acids, and chlorophyll. Nitrogen plays an important role in various plant processes such as photosynthesis, respiration, cell growth, and reproduction.
The role of nitrogen in plants
Nitrogen plays several roles in plants, including:
• Growth and development: Nitrogen is essential for plant growth and development. It helps produce proteins and nucleic acids, which are essential for building new cells and tissues. A nitrogen deficiency can lead to stunted growth, yellowing leaves, and reduced crop yield.
• Proteins: Proteins are the building blocks of plant cells and tissues. They also form enzymes that catalyze chemical reactions in plants.
• Nucleic acids: Nucleic acids, DNA and RNA, carry the genetic information of plants.
• Nitrogen deficiency: A nitrogen deficiency can lead to reduced synthesis of proteins and nucleic acids. This can lead to stunted growth, yellowing leaves, and reduced crop yield.
• Photosynthesis: Nitrogen is a major component of chlorophyll, the pigment that absorbs sunlight and uses it to produce energy. Nitrogen deficiency can lead to reduced photosynthesis and reduced energy production.
• Chlorophyll: Chlorophyll is found in the chloroplasts of plant cells. This pigment absorbs sunlight and uses it to convert
carbon dioxide and water into sugars and oxygen.
• Nitrogen deficiency: A lack of nitrogen can lead to a decrease in chlorophyll production. This can lead to a decrease in photosynthesis and a decrease in energy production.
• Respiration: Nitrogen is involved in the process of respiration. Respiration is the process by which plants release energy from sugars and other organic substances. A lack of nitrogen can lead to a decrease in respiration and a decrease in energy production. Respiration occurs in the mitochondria of plant cells. In this process, sugars and other organic substances react with oxygen to produce energy, carbon dioxide, and water.
• Reproduction: Nitrogen is essential for plant reproduction. This element helps in the production of seeds and fruits. A lack of nitrogen can lead to a decrease in the production of seeds and fruits.
• Seeds and fruits: Seeds and fruits contain proteins, nucleic acids, and other nutrients that are essential for the growth of new plants.
• Nitrogen deficiency: Nitrogen deficiency can lead to reduced production of proteins and nucleic acids in seeds and fruits. This can lead to reduced seed and fruit production.
| Read more: Use of carbon dioxide in urea production |
Nitrogen sources for plants
Plants can obtain nitrogen from a variety of sources, including:
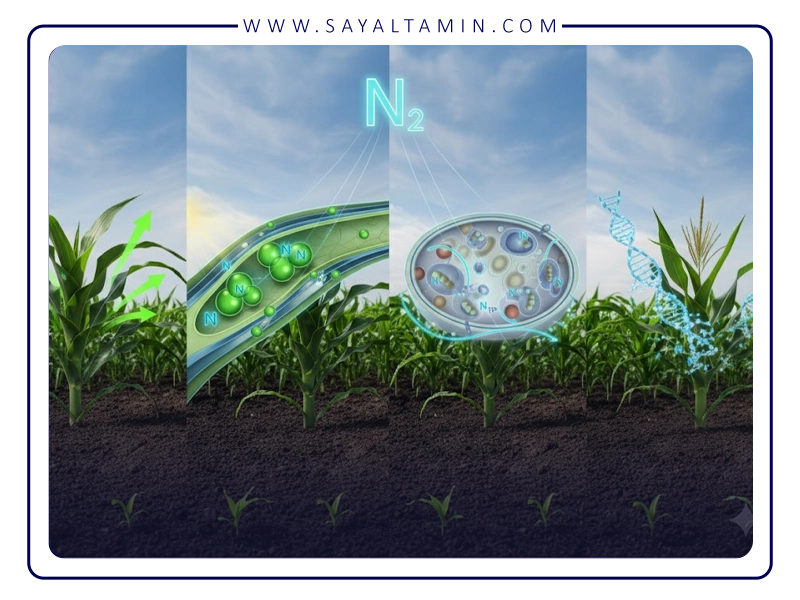
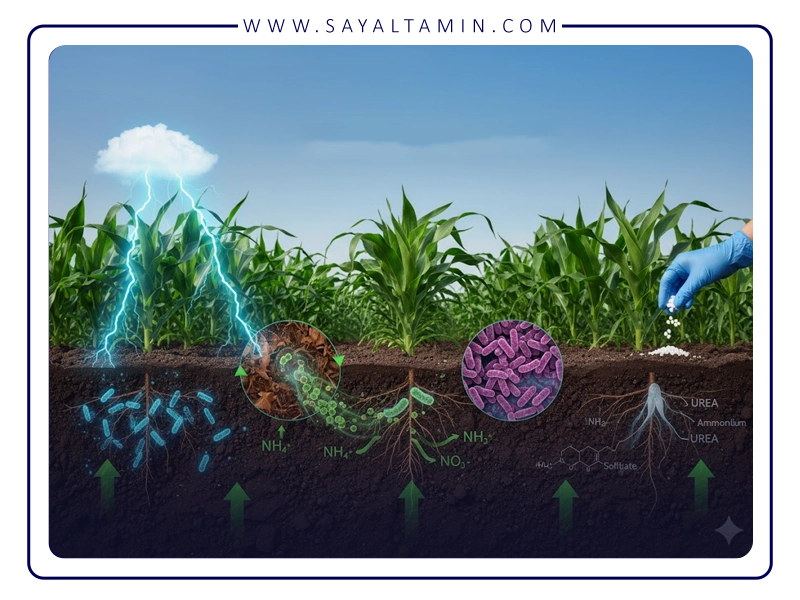
• Air: Nitrogen is the most abundant gas in the atmosphere, but plants cannot absorb it directly. Nitrogen-fixing bacteria in the soil can convert nitrogen from the air into a form that is usable by plants.
• Nitrogen-fixing bacteria: Nitrogen-fixing bacteria live in the soil in two forms: free-living and symbiotic. Free-living bacteria live independently in the soil and fix nitrogen. Symbiotic bacteria live in the roots of plants and fix nitrogen.
• Nitrogen fixation: Nitrogen fixation is the process by which nitrogen from the air is converted to ammonia (NH3). Ammonia is a form that is usable by plants.
• Soil: Soil contains organic and inorganic nitrogen. Organic nitrogen comes from the remains of dead plants and animals. Inorganic nitrogen is present in the soil in the form of nitrate (NO3-) and ammonium (NH4+).
• Organic nitrogen: Organic nitrogen must be converted by microbes in the soil into a form that is usable by plants. This process is known as mineralization.
• Inorganic nitrogen: Inorganic nitrogen is readily absorbed by plants. However, nitrate (NO3-) is easily leached from the soil. Ammonium (NH4+) remains in the soil longer, but can be converted to nitrate (NO3-).
• Fertilizers: Nitrogen fertilizers contain inorganic nitrogen that is readily absorbed by plants. Nitrogen fertilizers can help improve crop growth and yield.
• Types of Nitrogen Fertilizers: There are several types of nitrogen fertilizers, including urea, ammonium nitrate, ammonium sulfate, and organic fertilizers.
• Choosing the Right Fertilizer: Choosing the right fertilizer is important based on the needs of the crop and soil conditions.

Symptoms of nitrogen deficiency in plants
Nitrogen deficiency can lead to a variety of symptoms in plants, including:
• Slow growth: Plants with nitrogen deficiency grow slowly and may be shorter than normal.
• Yellowing leaves: The leaves of plants with nitrogen deficiency may turn yellow, especially the lower leaves.
• Reduced crop yield: Plants with nitrogen deficiency may have lower crop yields.
• Other symptoms: Other symptoms of nitrogen deficiency include: small leaves, narrow leaves, weak stems, and weak roots.
| Must Read: Use of Liquid Nitrogen in the Construction and Civil Engineering Industry |
Nitrogen management in agriculture
Proper nitrogen management in agriculture is essential to ensure optimal crop growth and yield. Nitrogen management includes the following:
• Choosing the right fertilizer: It is important to choose the right fertilizer based on the crop needs and soil conditions.
• Fertilization timing: Fertilization timing should be such that plants receive nitrogen at the appropriate time.
• Fertilizer amount: The amount of fertilizer should be such that it meets the needs of the plants, but excessive use of fertilizer should be avoided.
• Use of nitrogen fixation methods: Using nitrogen fixation methods such as growing nitrogen-fixing plants can help reduce the need for nitrogen fertilizers.
• Other nitrogen management methods: Other nitrogen management methods include: crop rotation, use of green manure, and use of efficient irrigation methods.

Nitrogen is an essential element for plant growth and development. Proper nitrogen management in agriculture is essential to ensure optimal crop growth and yield.
————————————————–
References