This post is also available in: Persian Armenian
The steel industry is one of the most fundamental and vital sectors worldwide, playing a key role in economic development and industrial infrastructure. Improving steel quality, enhancing production efficiency, and focusing on environmental sustainability have always been major concerns in this industry. Various industrial gases are involved in steel production, with nitrogen being one of the most important and versatile gases.
Due to its unique properties, such as inertness, abundance, high purity availability, and relatively low cost, nitrogen plays a multifaceted and essential role in various steelmaking processes. From being added as an alloying element to serving as a protective gas in furnaces and surface heat treatment, nitrogen enhances the quality, durability, and performance of steel.
One of the key sources of nitrogen supply is gas condensates. Gas condensates, a by-product of natural gas extraction, contain various gases. Through advanced separation technologies, high-purity nitrogen is extracted and used in industries, especially steelmaking. This supply source is crucial for companies active in the field of gas condensate supply, as ensuring the quality and stability of nitrogen supply can improve the quality of steel products and the efficiency of production processes.
This paper reviews the diverse applications of nitrogen in steelmaking and analyzes the benefits, challenges, and future of this important gas in the steel industry.
Nitrogen as an Alloying Agent
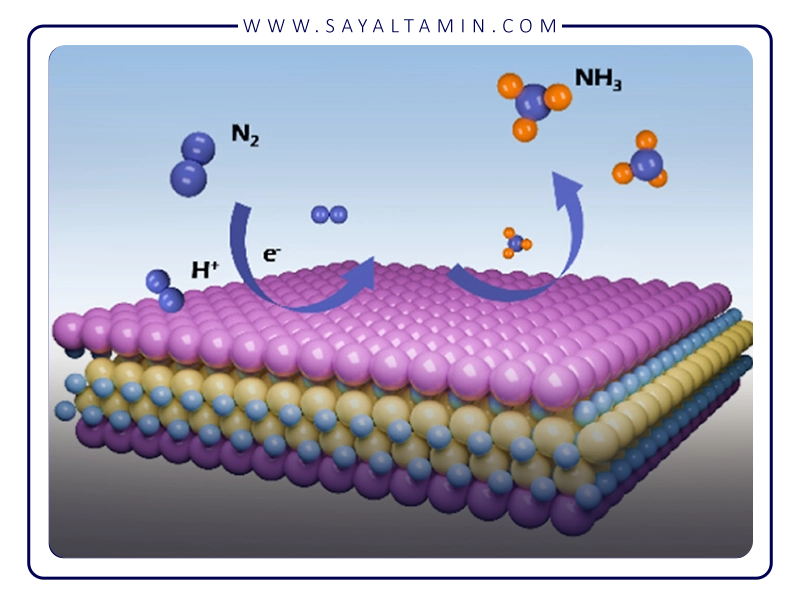
One of the most important applications of nitrogen in steelmaking is its role as an alloying element. Adding nitrogen to steel not only positively impacts mechanical properties but also significantly improves resistance to corrosion and extends the lifespan of steel products.
Effect of Nitrogen on Steel’s Mechanical Properties:
Nitrogen distributes itself in steel as very fine and uniform nitrides within the steel matrix. These nitrides act as barriers to grain growth, thereby increasing tensile strength and hardness. This property is particularly significant in the production of high-strength low-alloy (HSLA) steels, which are used in the automotive industry, oil and gas pipelines, and construction structures.
In addition to increasing strength, the presence of nitrogen in steel also enhances wear resistance, which prolongs the life of industrial components and reduces maintenance costs. Nitrogen also improves fatigue resistance, which is crucial for parts subjected to cyclic loading.
Nitrogen and Corrosion Resistance:
In austenitic stainless steels, nitrogen is used as an economical and effective replacement for nickel. This element stabilizes the austenitic structure, thereby enhancing corrosion resistance, particularly against localized and pitting corrosion. These steels are widely used in chemical, marine, and medical equipment industries.
Increasing the stability of the oxide layer on the surface of stainless steels through the presence of nitrogen, especially in corrosive and aggressive environments, enhances the performance of these steels and reduces the need for coatings or frequent maintenance, resulting in cost savings and reduced environmental impact.
Nitrogen Gas from Gas Condensates and its Importance in Steelmaking

Sources of Nitrogen Supply:
The nitrogen used in steelmaking industries is typically supplied from several sources, with the most important being air separation and extraction from gas condensates. Gas condensates, a by-product of natural gas and oil extraction processes, contain various gaseous compounds such as methane, ethane, propane, butane, and nitrogen.
Using advanced technologies such as Pressure Swing Adsorption (PSA), chemical absorption, and cryogenic distillation, high-purity nitrogen is extracted from gas condensates. The purity of this nitrogen is crucial for its application in steel production.
| Read more: Use of oxygen in the steel industry |
Importance of Stable and Quality Nitrogen Supply:
For gas condensate suppliers, providing high-quality and stable nitrogen is a priority. Nitrogen with the specified purity and conditions must be supplied to steel industries to ensure optimal performance and product quality. Additionally, providing nitrogen with appropriate purity and minimal contamination is key in improving steelmaking processes.
For instance, impurities such as oxygen or moisture in nitrogen gas can cause problems like oxidation or changes in steel properties, negatively affecting the final product’s quality.
Nitrogen as a Protective Gas in Steelmaking Processes
Importance of Protective Gas in Steelmaking:
In steelmaking processes, particularly in Electric Arc Furnaces (EAF) and Ladle Metallurgy Furnaces (LMF), the presence of a protective gas is essential to prevent molten steel from reacting with oxygen, nitrogen, and other atmospheric gases. These reactions can lead to the formation of oxides, nitrides, and hydrogen embrittlement, which reduce the mechanical properties of steel.
Nitrogen, due to its inert nature, is one of the best options for this purpose, as it protects the molten steel while maintaining the steel’s quality and purity.
Use in Electric Arc Furnace (EAF):
In the electric arc furnace process, the injection of nitrogen creates a protective atmosphere that prevents steel oxidation. This helps reduce slag consumption and maintains alloying elements, improving material recovery efficiency.
Moreover, the use of nitrogen reduces the emission of greenhouse gases and environmental pollutants associated with steelmaking processes, contributing to enhanced environmental sustainability.
Stirring Molten Steel in Ladle Metallurgy Furnace (LMF):
In the ladle metallurgy furnace process, nitrogen is used as a stirring agent to homogenize molten steel. Nitrogen bubbling into the molten steel ensures uniform distribution of chemical composition, temperature, and dissolved gases.
This process also aids in removing dissolved gases such as hydrogen, preventing internal defects and brittleness in steel, thus improving the final product’s quality and performance.
Nitriding
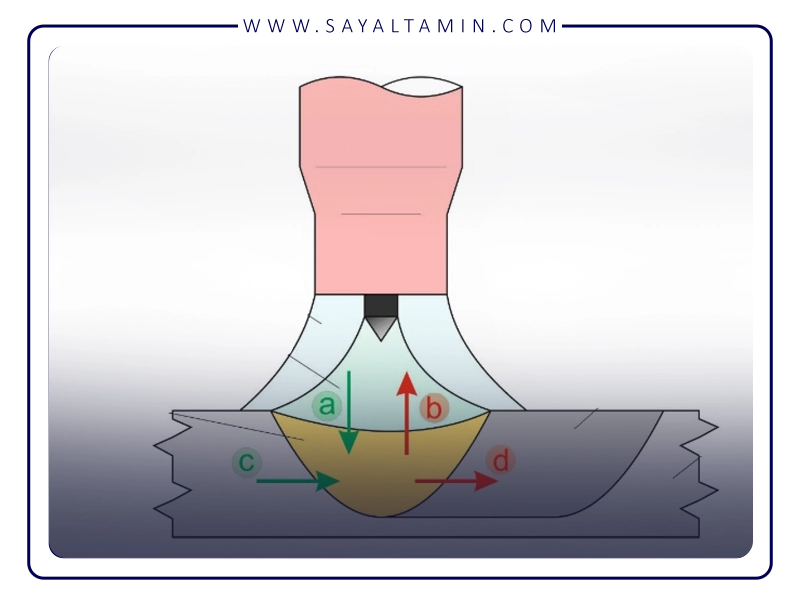
Definition and Application of Nitriding:
Nitriding is a surface heat treatment process in which nitrogen diffuses into the surface of steel, creating a hard, wear- and corrosion-resistant layer. This surface layer significantly increases the lifespan and performance of parts used in harsh working conditions.
Nitriding is typically carried out at lower temperatures compared to other surface hardening processes like carburizing, reducing distortion and dimensional changes in parts.
Advantages of Nitriding over Traditional Methods:
Maintaining core toughness: Nitriding hardens the surface without reducing the flexibility and internal strength of the part.
Reduced distortion and dimensional changes: Due to the lower operating temperature, parts undergo less shape distortion.
Increased fatigue and wear resistance: The nitrided hard layer increases the durability of parts under cyclic loading conditions.
Improved corrosion resistance: The nitrided layer protects steel from corrosive environments.
These benefits have made nitriding widely used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, tool manufacturing, and die making.
Environmental Benefits of Using Nitrogen in Steelmaking
The use of nitrogen in steelmaking not only provides significant technical advantages but also helps in maintaining environmental sustainability in the steel industry:
Reduction in pollutant emissions: Using nitrogen as a protective gas reduces the production of greenhouse gases and pollutants caused by oxidation and combustion.
Prevention of hazardous waste generation: Improving steel quality and reducing the need for finishing operations and protective coatings reduces industrial waste and harmful chemical consumption.
Increased lifespan of steel products: Enhancing corrosion and wear resistance of nitrided steels reduces the frequency of part replacements and decreases the consumption of natural resources.
Energy consumption reduction: Optimizing steelmaking processes with nitrogen reduces energy consumption and increases efficiency.
| Must read: Use of Argon in the Steel Industry |
Challenges and Technical Solutions for Optimizing Nitrogen Use

While nitrogen has numerous applications and significant benefits, its optimal and controlled usage presents certain challenges:
. Precise control of nitrogen content in steel: The amount of nitrogen must be carefully controlled to ensure the desired properties are achieved without negatively affecting weldability or toughness.
. Optimizing nitrogen injection rates and methods: Overuse or underuse of nitrogen in furnace processes can have negative effects. The design of nozzles, injection rates, and injection locations must be meticulously planned.
. Continuous and quality nitrogen supply: Fluctuations in gas purity or supply levels can negatively affect the quality of steel. Close cooperation with gas condensate suppliers and the use of advanced separation technologies are essential.
. Training and utilizing skilled personnel: Using nitrogen in complex processes requires technical knowledge and expertise, which must be continuously updated.
Future Prospects and Innovations in Nitrogen Use
With advances in gas separation technologies and increasing attention to sustainability and environmental concerns, nitrogen’s applications in steelmaking are expected to grow:
Development of new nitrogen separation technologies with higher yields and quality from gas condensates.
Wider use of nitrided steels in advanced industries like lightweight automotive, aerospace, and medical equipment.
Optimization of nitrogen injection and application processes through artificial intelligence and advanced control systems.
Focus on reducing energy consumption and pollutants through the design of more eco-friendly processes.
Development of combined nitriding processes with new technologies for better mechanical and surface properties.
Nitrogen, as a versatile and crucial gas in steelmaking, plays a vital role in improving mechanical properties, increasing corrosion resistance, optimizing processes, and maintaining environmental sustainability. The use of nitrogen as an alloying element, protective gas, and nitriding agent significantly enhances steel quality and durability, helping reduce costs and environmental impact.
Given the importance of sustainable and high-quality nitrogen supply from sources like gas condensates, close collaboration between steel manufacturers, gas suppliers, and research centers is essential for developing innovative technologies and optimizing processes. The future of the steel industry, driven by intelligent nitrogen use, looks bright and promising.
———————————————
References
1.www.ispatguru.com
2. H. K. D. H. Bhadeshia, “Nitrogen in steels: effects and applications,” International Materials Reviews, 2001.
3. G. E. Totten, “Steel Heat Treatment: Metallurgy and Technologies,” CRC Press, 2006.




