This post is also available in: Persian Armenian
Oxygen is an essential element for life and the proper functioning of the human body. However, in medical science, oxygen plays a far more extensive and complex role, especially in advanced therapeutic approaches such as Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT). This treatment involves breathing 100% pure oxygen at pressures exceeding atmospheric levels, leading to significant advancements in managing various diseases and injuries. This article comprehensively explores the applications of oxygen gas in HBOT, its mechanisms of action, clinical benefits, and the critical importance of using pure oxygen under hyperbaric conditions.
What is Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy?
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT) is a cutting-edge medical treatment where patients breathe 100% oxygen inside a specially designed chamber at pressures typically ranging from 2 to 3 times atmospheric pressure. The principle underlying this therapy is based on Henry’s Law, which states that the solubility of a gas in a liquid (such as blood plasma) increases proportionally with pressure.
Under normal conditions, oxygen is primarily transported by hemoglobin in the blood. However, in HBOT, the elevated pressure allows a significantly higher amount of oxygen to dissolve directly into the plasma. This enhanced oxygen delivery is particularly effective in reaching tissues with compromised blood flow or those affected by injury or inflammation, where oxygen supply is usually insufficient.
Mechanisms of Action of Oxygen Under Hyperbaric Conditions

Oxygen exerts its therapeutic effects in HBOT through several key mechanisms:
Enhanced Oxygen Delivery to Tissues
Increased oxygen pressure substantially elevates the amount of oxygen dissolved in plasma, enabling delivery to hypoxic or ischemic tissues that hemoglobin-bound oxygen cannot sufficiently reach. This plays a vital role in tissue repair and preventing further damage.
Reduction of Inflammation and Immune Modulation
HBOT reduces the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines while promoting anti-inflammatory mediators, thereby modulating the immune response. It mitigates inflammation in damaged areas and prevents secondary tissue injury. Furthermore, HBOT optimizes immune cell function, enhancing neutrophil activity against infections without harming healthy tissues.
Stimulation of Angiogenesis (New Blood Vessel Formation)
The abundant oxygen supply in HBOT stimulates the formation of new blood vessels in damaged tissues, improving blood flow and accelerating wound healing.
Antimicrobial Effects
Hyperbaric oxygen exhibits bactericidal properties, particularly against anaerobic bacteria. This makes HBOT an effective adjunctive therapy for severe infections such as gas gangrene and clostridial myonecrosis.
Treatment of Poisonings
HBOT is especially effective in carbon monoxide poisoning by rapidly displacing carbon monoxide from hemoglobin, thereby reducing tissue hypoxia and preventing fatal outcomes.
Clinical Applications of Oxygen in HBOT
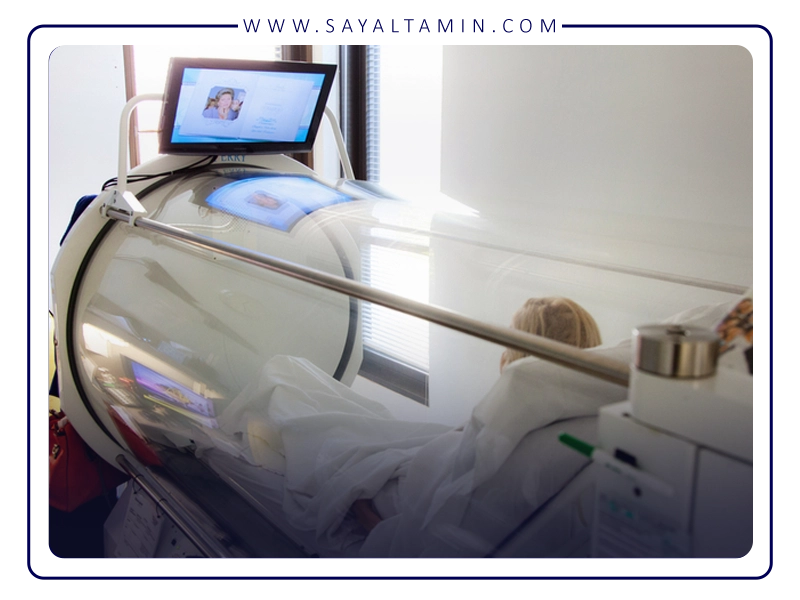
HBOT is widely employed across diverse medical fields with significant clinical benefits:
Chronic and Diabetic Wounds
One of the most common uses of HBOT is in the treatment of chronic diabetic foot ulcers and other non-healing wounds. These wounds often suffer from poor blood circulation and severe inflammation. HBOT enhances oxygen delivery and promotes angiogenesis, speeding up healing and reducing the risk of limb amputation.
Soft Tissue and Bone Infections
In severe infections like gas gangrene and osteomyelitis, HBOT serves as an adjunct therapy to control infection progression by creating an inhospitable environment for anaerobic bacteria and boosting immune defense.
Decompression Sickness
Commonly seen in divers, this condition results from gas bubbles forming in the bloodstream. HBOT facilitates bubble dissolution and alleviates symptoms by increasing ambient pressure and oxygen availability.
Carbon Monoxide Poisoning
HBOT accelerates the removal of CO from hemoglobin and limits damage to vital organs in cases of acute poisoning.
Mitigating Radiation Therapy Side Effects
HBOT reduces radiation-induced tissue injury by enhancing tissue oxygenation and promoting repair, improving patient recovery.
Severe Burns
In extensive burns, HBOT decreases edema, improves microcirculation, and speeds tissue regeneration.
Sudden Sensorineural Hearing Loss
HBOT may improve hearing by restoring oxygen supply to the inner ear, potentially reversing sudden hearing loss.
| Be sure to read: What is cryotherapy? |
Advantages of Using Pure Oxygen Under Hyperbaric Conditions
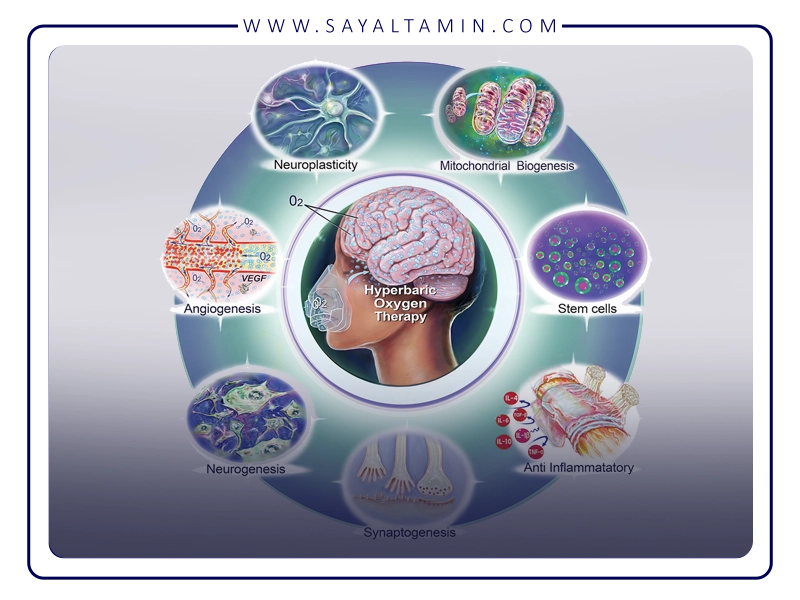
Enhanced Therapeutic Efficacy
The substantial increase in oxygen partial pressure results in more oxygen dissolved in plasma and tissues, maximizing therapeutic outcomes.
Reduced Dependence on Pharmaceuticals
HBOT often reduces the need for antibiotics and anti-inflammatory drugs, minimizing medication-related side effects.
Improved Patient Quality of Life
Faster recovery times, reduced complications, and less invasive treatment modalities contribute to better overall patient wellbeing.
| Read more: Use of oxygen gas in oxygen therapy for migraines |
Important Considerations for HBOT
Patient Selection
Careful assessment is essential to identify appropriate candidates and exclude those with contraindications or high risk of adverse effects.
Medical Supervision
HBOT should be administered under strict clinical monitoring to promptly manage any potential complications.
Use of Standardized Equipment
Employing certified hyperbaric chambers and reliable equipment ensures safety and treatment effectiveness.
Patient Education
Informing patients about the procedure, benefits, and potential risks enhances compliance and treatment success.
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT), through the administration of pure oxygen at elevated pressures, stands as one of the most effective therapeutic interventions for a broad range of medical conditions. Its ability to augment tissue oxygenation, reduce inflammation, stimulate healing processes, and exert antimicrobial effects makes it invaluable in modern medicine. Ongoing advancements in HBOT technology and research continue to expand its clinical applications, reinforcing its crucial role in contemporary healthcare.
————————————————–
References




