This post is also available in: Persian Armenian
In today’s industrial world, the use of nitrogen gas in manufacturing and laboratory processes has gained a special place. Nitrogen gas, due to its unique properties, is vital as an inert and non-flammable gas in many industries. One of the important applications of this gas is its use in graphite furnaces, which are used in various industries such as metallurgy, scientific research, chemical laboratories and the production of advanced materials.
Graphite furnaces play an important role in the production and analysis of materials due to their high thermal conductivity, good mechanical strength and chemical stability at very high temperatures. These furnaces are capable of performing processes such as melting metals, synthesizing new materials and analyzing chemical compounds. In this article, we will fully examine the role and importance of nitrogen gas in graphite furnaces, describe its practical applications and analyze the advantages of using this gas. Also, safety tips and operational standards related to the use of nitrogen are reviewed to provide a comprehensive and practical picture for non-specialist audiences.
| Read more: Use of argon as a shielding gas in graphite furnaces |
Introduction to graphite furnaces
Definition and structure of graphite furnaces
Graphite furnaces are devices designed to produce very high heat and control temperature precisely. The main material in this type of furnace is graphite, which is considered the best option for industrial and laboratory environments due to its high thermal conductivity, resistance to high temperatures, and chemical stability.
The structure of graphite furnaces consists of a chamber in which the sample or material of interest is placed. This chamber is usually made of pure graphite or a combination of graphite with other resistant materials to withstand high temperatures. The heat required to carry out the processes is provided using electricity, induction furnaces or special fuels. The internal temperature of these furnaces can reach thousands of degrees Celsius and cause melting, chemical reactions or decomposition of materials.
Types of graphite furnaces and their applications
Graphite furnaces are produced in different types, and each type has its own characteristics and applications. Understanding the types of furnaces and the advantages and disadvantages of each plays an important role in choosing the most suitable furnace for any industrial or research process.
• Graphite induction furnaces: These furnaces use magnetic fields to generate heat and are mainly used in the melting of metals and alloys. Their main advantage is precise temperature control and reduced energy consumption.
• Electric arc furnaces: These types of furnaces are capable of producing very high temperatures and are used to synthesize advanced materials such as carbides and heat-resistant compounds.
• Laboratory furnaces: These are small, controlled furnaces used in scientific research and materials analysis. These furnaces are capable of producing high temperatures with great precision and provide a suitable environment for conducting precise experiments.

The importance of choosing the right furnace
Choosing the right furnace depends on the type of material, the required temperature, and the purpose of the process. Using an inappropriate furnace can reduce product quality, increase energy costs, and even damage equipment. Therefore, in advanced industries and laboratories, special attention to the design and type of furnace is very important.
Properties of nitrogen gas
Physical and chemical properties of nitrogen
Nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, and nontoxic gas that makes up about 78 percent of the Earth’s atmosphere. It is nonflammable and does not chemically react with many substances under normal conditions. For this reason, nitrogen is considered a neutral gas and is widely used in environments that prevent oxidation.
Nitrogen can also be used in liquid form. Liquid nitrogen has a very low temperature and is used as a coolant in industrial and laboratory processes. This property allows for precise temperature control and prevents unwanted reactions in furnaces.
Industrial nitrogen production
Nitrogen gas is mainly produced through the fractional distillation of air. In this process, air is first liquefied and then its components, such as nitrogen and oxygen, are separated by their boiling point differences.
There are other methods for industrial nitrogen production, including:
• Pressure swing adsorption (PSA) method: In this method, oxygen and other gases are separated from nitrogen by absorbent materials.
• Membrane method: In this method, air passes through membranes that allow nitrogen to pass through and separate other gases.
The choice of nitrogen production method depends on the volume required and the expected purity.
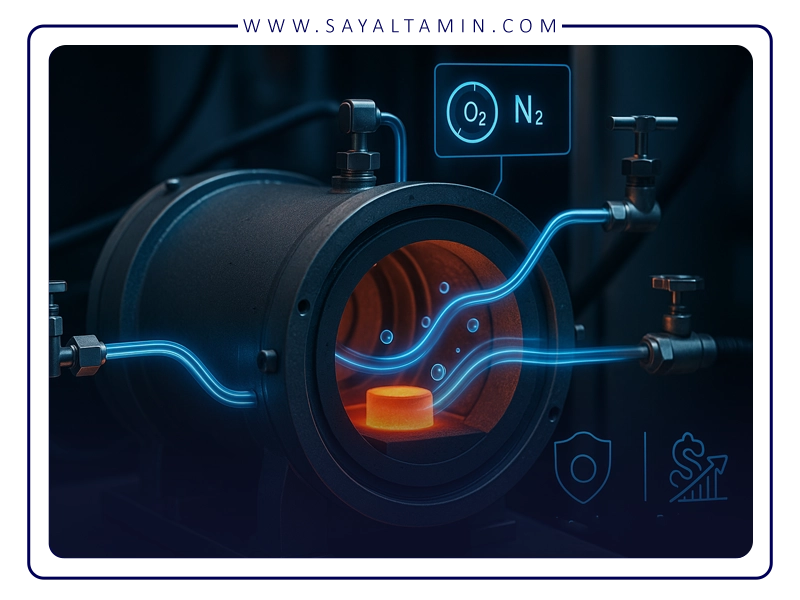
Use of nitrogen gas in graphite furnaces
Creating an ineffective environment
One of the most important uses of nitrogen is to create an inert environment in a furnace. When nitrogen is injected into a furnace, the oxygen content is reduced and unwanted reactions such as oxidation of metals or chemical compounds are stopped. This feature increases the quality of products and prevents waste and unwanted changes.
In the metal industry, this application is of particular importance because even small amounts of oxygen can cause surface oxides and reduce the quality of the final product.
Temperature and pressure control
Nitrogen can play an important role in controlling the temperature and pressure inside the furnace. Due to its high heat capacity, nitrogen acts as a cooling agent and prevents unwanted temperature fluctuations. This property is especially critical in sensitive laboratory processes that require high temperature accuracy.
Use in Graphite Furnace Atomic Absorption Apparatus
In Graphite Furnace Atomic Absorption Apparatus (GFAAS), nitrogen is used as a carrier gas to transport samples to the thermal zone. This application increases the accuracy and sensitivity of the analysis and allows the detection of elements at very low concentrations. Nitrogen creates a stable and controlled environment for performing precise analyses.
Advantages of using nitrogen in graphite furnaces
Increase equipment life
The use of nitrogen reduces oxidation and corrosion of furnace components. When the environment inside the furnace is inert with nitrogen, direct contact of the materials with oxygen is reduced and the corrosion process is minimized. This increases the useful life of the equipment and reduces the need for frequent repairs or replacement of parts.
For example, in the metal industry, where furnaces are used to melt oxygen-sensitive alloys, the presence of nitrogen preserves the properties of the alloys and prevents damage to the electrodes and furnace walls. This directly reduces maintenance costs and increases productivity.

Improving product quality
The inert environment created by nitrogen allows for the production of higher quality products with more desirable properties. The materials in the furnace are less affected by air, moisture, and oxygen, and their chemical composition is preserved.
For example, in the production of precious metals or semiconductor materials, even a small percentage of oxygen can cause surface defects or change chemical properties. The use of nitrogen allows the final product to be produced with high precision and quality and reduces scrap rates.
Reduce costs and increase productivity
The use of nitrogen reduces maintenance and repair costs and increases process efficiency. Reducing waste, extending equipment life, and improving product quality directly result in financial savings and increased profitability for industries.
In addition, precise temperature and pressure control with the help of nitrogen reduces energy waste and optimizes the consumption of electricity or fuel required for furnace heating. This is especially important in large industries and factories with high energy consumption.
Specific applications in advanced industries
Nitrogen is also used in advanced industries such as the production of electronic components, advanced ceramics, and composite materials. In these industries, the inert environment with nitrogen helps to limit unwanted chemical reactions and preserve the properties of the materials.
For example, in the production of carbon fibers and advanced graphite materials, the use of nitrogen helps reduce cracks and increase the mechanical strength of products. Also, in precision chemical analysis and atomic absorption, nitrogen provides a stable and controllable environment for making precise measurements.
Safety tips when using nitrogen
Although nitrogen is safe under normal conditions, its improper use can pose risks. Nitrogen can replace oxygen in the environment and cause suffocation. Therefore, it is essential to follow safety precautions when using nitrogen in furnaces and industrial environments.
Proper ventilation and protective equipment
Ensuring proper ventilation, the use of masks and respirators, and safety equipment are essential. Employees should be trained on what to do in the event of a nitrogen leak and what steps to take to maintain safety.
Warning systems
It is important to install oxygen and nitrogen gas alarm sensors in industrial and laboratory environments. These systems monitor the amount of oxygen available and warn when oxygen levels decrease so that employees can react in a timely manner.
Operational protocols
It is essential to have specific operating instructions and protocols for filling, maintaining, and using nitrogen tanks. These protocols include safety guidelines, tank handling, and emergency procedures. Following these guidelines will minimize the risks associated with liquid or gaseous nitrogen.
Environmental impacts and the place of nitrogen in advanced technologies
Nitrogen, being neutral, has no direct impact on the environment and its use in industrial processes does not cause chemical pollution. This characteristic has given nitrogen a special place in green industries and sustainable technologies.
In advanced technologies such as semiconductor manufacturing, clean energy, and advanced materials, nitrogen is used as a safe and stable environment to control reactions and protect the quality of materials. In scientific research, nitrogen also enables precise experiments with high repeatability.
Real-world practical and industrial examples of nitrogen use in graphite furnaces
In various industries, nitrogen is widely used to improve quality and control processes in graphite furnaces. Some real examples are:
• Metal industries: In the melting of oxygen-sensitive alloys such as titanium and nickel alloys, nitrogen is injected as an inert gas into graphite furnaces. This prevents oxidation of the metal surface and preserves the mechanical properties of the alloys.
• Semiconductor industries: In the production of silicon and semiconductor materials, an inert environment with nitrogen prevents unwanted reactions and increases the quality of the crystals produced.
• Production of carbon fibers and composite materials: Nitrogen creates a stable environment during the carburization process of carbon fibers and prevents cracks and structural defects.
• Laboratory research: In atomic absorption and thermal analysis of chemical samples, nitrogen acts as a carrier gas and protects the samples, which increases the accuracy and repeatability of the experiments.
These examples show that nitrogen is vital in various industries not only for protecting materials but also for improving process performance and product quality.
| Must read: Use of nitrogen gas in steelmaking |
Other methods of nitrogen injection and control
The effective use of nitrogen in graphite furnaces depends on the method of injection and its careful control. Some important points are:
• Continuous injection: In this method, nitrogen is continuously introduced into the furnace to ensure that the environment inside remains inert at all times. This method is suitable for processes that require high temperatures and long-term chemical stability.
• Staged injection: Nitrogen is injected only at critical stages of the process, such as during melting or chemical reactions. This method reduces gas consumption and is suitable for short-term or laboratory processes.
• Pressure and flow control: The use of valves and automatic systems to regulate the flow and pressure of nitrogen creates a stable environment and prevents unwanted fluctuations in temperature and pressure.
• Real-time monitoring: Using sensors and online monitoring, the oxygen and nitrogen levels in the furnace are monitored to prevent the development of unwanted conditions.
These methods ensure that nitrogen is operating effectively and the quality of the process and products is maintained.
Comparison between types of furnaces and the effect of nitrogen on each
The effects and benefits of nitrogen vary across different types of graphite furnaces. The following comparison helps to better understand the application of nitrogen for each type of furnace:
Furnace type Nitrogen advantage Main application in industries
Graphite induction furnace Creating an inert environment to prevent oxidation, temperature control Melting of metals and alloys sensitive to oxygen
Electric arc furnace Protecting materials at very high temperatures, preventing unwanted reactions Synthesis of carbides and advanced materials
Laboratory furnace Maintaining a stable environment for accurate analysis, increasing the sensitivity of measurements Scientific research and sample analysis
As can be seen, nitrogen has its own specific role in each type of furnace and its optimal use depends on the type of process and industrial purpose.
Practical recommendations
Nitrogen gas, with its unique properties, plays a vital role in the optimal operation of graphite furnaces. The benefits of using nitrogen include extending equipment life, improving product quality, reducing costs, and increasing process efficiency. Also, creating an inert environment reduces waste and preserves the chemical properties of materials.
Compliance with safety precautions and the use of warning systems, proper ventilation, and operational protocols ensure the safety of employees and the work environment. Nitrogen is used not only in traditional industries but also in advanced technologies and scientific research, and is considered a key gas in industrial and laboratory processes.
The correct and safe use of nitrogen increases product quality and process efficiency, saves money and protects equipment. Attention to the properties and applications of nitrogen is essential for success in industries related to graphite furnaces, and the future use of this gas in advanced industries promises further scientific and industrial advances.
————————————————–
Sources:
– www.carbolite-gero.com
– www.superbheating.com
– www.vacuum-furnaces.com
– www.airbestpractices.com




