This post is also available in: Persian Armenian
Chromatography, as one of the most powerful and widely used techniques for the separation and analysis of chemical compounds, plays an important role in various fields such as analytical chemistry, pharmaceutical industries, environment, and quality control. One of the important branches of this technique is gas chromatography or (GC), which is used to analyze volatile or semi-volatile compounds. The quality and efficiency of this method largely depend on the choice of carrier gas. Among them, nitrogen gas has become one of the most widely used options due to its special properties and many advantages. In this article, we will deeply examine the application, advantages, limitations, and key points related to the use of nitrogen gas in gas chromatography.
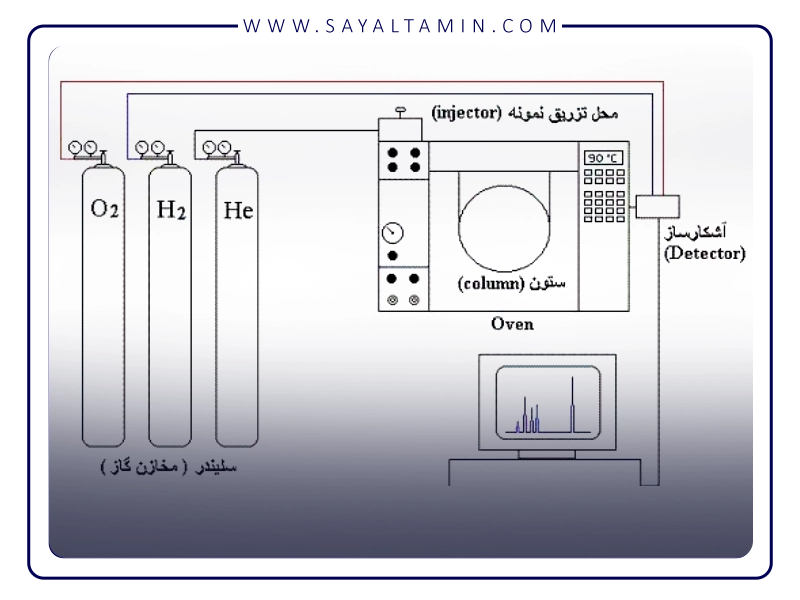
Properties of nitrogen gas and its role in gas chromatography
Nitrogen (N₂) is a colorless, odorless, and relatively inert gas that makes up about 78% of atmospheric air. With a molecular weight of about 28 g/mol, this gas has favorable physical and chemical properties that make it ideal for use as a mobile phase in gas chromatography.
- High purity and wide availability:
Nitrogen with a purity of 99.999% is easily separated from air and produced in large volumes. This level of purity is particularly important to prevent noise and ghost peaks in the instrument and ensure the accuracy and precision of analytical results.
- Chemical stability:
Nitrogen is much less reactive than many other carrier gases and does not react with sample components or chromatography column materials. This property helps preserve sample structure and instrument stability.
- Suitable molecular weight and viscosity:
The average molecular weight of nitrogen creates a uniform flow in the chromatography column, which leads to optimal peak separation and accurate reproducibility of results.
- High safety and economical cost:
Unlike hydrogen, which is a flammable gas, nitrogen is a non-flammable and safe gas. It is also more economical than helium, which is in limited supply and expensive. These two characteristics have made nitrogen a popular choice in many laboratories and industries.
Specialized applications of nitrogen gas in various types of gas chromatography
Nitrogen is used as a carrier gas in a wide range of gas chromatography applications, including:
- Gas chromatography with thermal conductivity detectors (TCD): TCD is sensitive to changes in the thermal conductivity of the carrier phase. Since the thermal conductivity of nitrogen is relatively low, changes due to the presence of sample compounds are well detected, making this detector suitable for use with nitrogen.
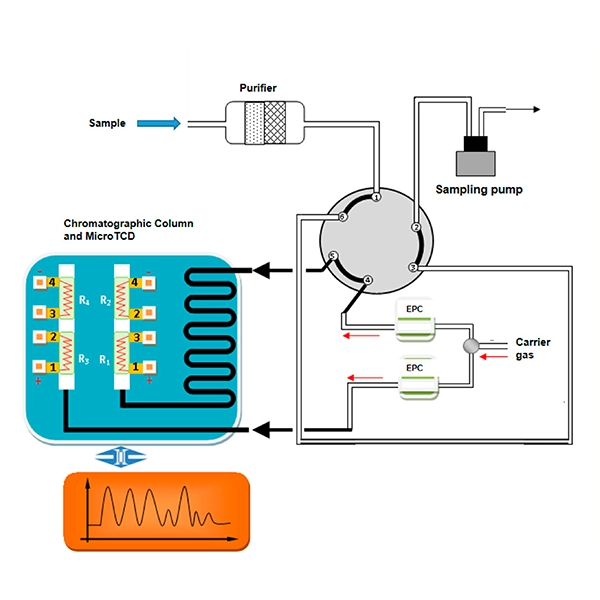
- Gas chromatography with flame ionization detectors (FID): While FID is mainly used for the analysis of hydrocarbons using hydrogen gas as an auxiliary gas, nitrogen can also be used as a carrier gas alongside hydrogen and air in the FID system.
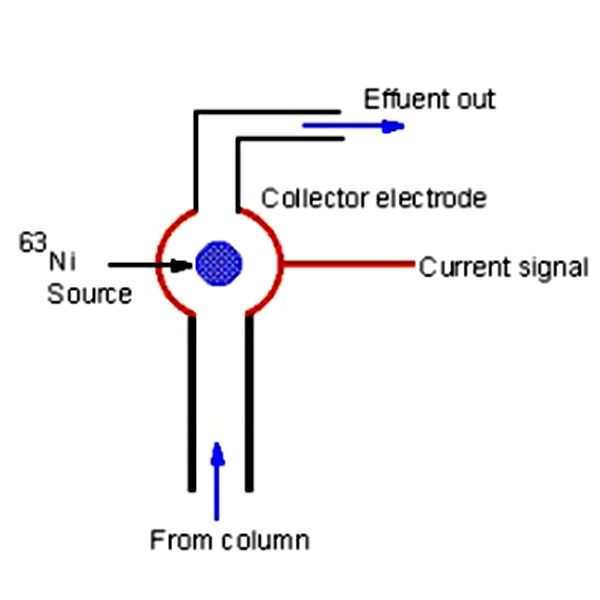
- Gas chromatography with electron acceptor detectors (ECD): ECD is sensitive to electrophilic compounds. Nitrogen is a good choice for this type of detector due to its high purity and lack of electronically active compounds.
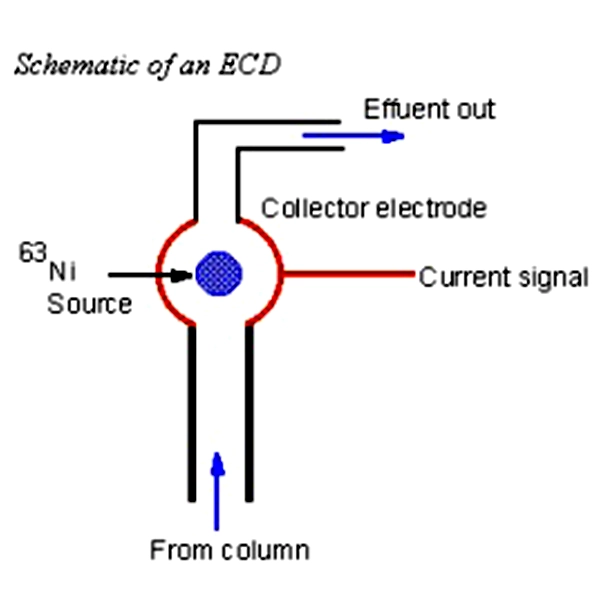
- Capillary GC: Capillary GC, which uses columns with small internal diameters, requires a very precise and controlled flow of carrier gas. Nitrogen, with its ability to achieve an optimal flow rate, allows for high-resolution separations in this type of column.
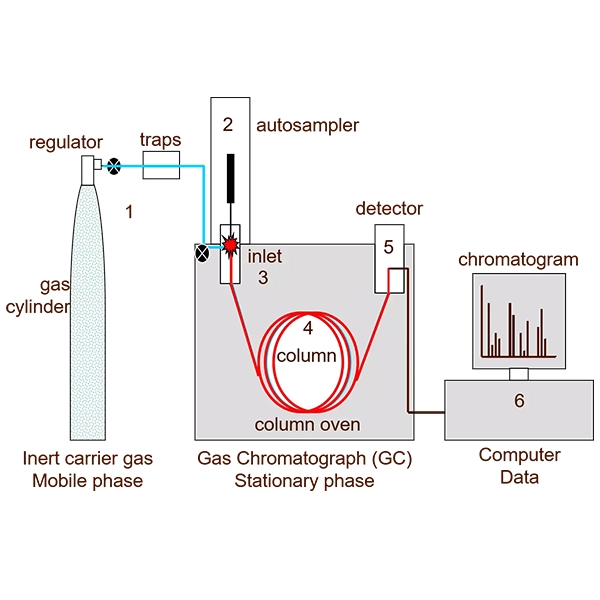
Advantages and benefits of nitrogen gas in chromatography
- Easy access and possibility of on-site production:
Using nitrogen generators, this gas can be produced continuously and cost-effectively on-site in the laboratory, which significantly reduces costs.
- Wide compatibility:
Nitrogen is compatible with a variety of commercial detectors and columns and performs well in separating polar and nonpolar compounds.
- High safety:
By being non-flammable, the risk of unwanted accidents is reduced and safer working conditions are created.
- Long-term sustainability:
Due to the lack of reaction with the column stationary phase or samples, the useful life of the column is extended and maintenance costs are reduced.
Limitations and disadvantages of using nitrogen
Despite its many advantages, the use of nitrogen in gas chromatography also comes with some limitations:
- Slower transfer rate than hydrogen and helium: Due to its higher molecular weight, nitrogen has a slower transfer rate through the column than hydrogen and helium. This can lead to longer analysis times and poorer resolution in some cases, especially for compounds with long retention times.
- Poorer performance in long columns: In long gas columns, the velocity difference between nitrogen and hydrogen/helium becomes more pronounced and can lead to reduced efficiency.
- Lower sensitivity in some detectors: For some very sensitive detectors that require rapid changes in thermal conductivity or ionization, hydrogen or helium may be a better choice.
- Potential for moisture and oxygen: Although high-purity commercial nitrogen is available, the presence of trace amounts of moisture or oxygen can negatively affect column performance and detector sensitivity. The use of appropriate filters is essential to remove these impurities.
Practical considerations in using nitrogen
To achieve the best results when using nitrogen as a carrier gas in gas chromatography, the following points should be considered:
- Use quality regulators: To ensure a steady, undisturbed flow, it is vital to use high-quality, high-pressure regulators for your nitrogen cylinder.
- Leak-free piping and connections: Any leaks in the system can lead to pressure loss, air ingress, and contamination. Regular inspection of connections and use of appropriate sealants are essential.
- Use of purification filters: To remove impurities such as moisture, oxygen, and hydrocarbons from the nitrogen stream, it is recommended to use special carrier gas purification filters.
- Optimal flow rate adjustment: The carrier gas flow rate should be optimized based on the column type, column configuration, and nature of the sample to achieve the best resolution and shortest analysis time.
- Choosing the right detector: Given the limitations of nitrogen, it is important to choose a detector that is compatible with its characteristics.
Comparison of nitrogen with other carrier gases
In gas chromatography, in addition to nitrogen, helium (He) and hydrogen (H2) are also commonly used as carrier gases.
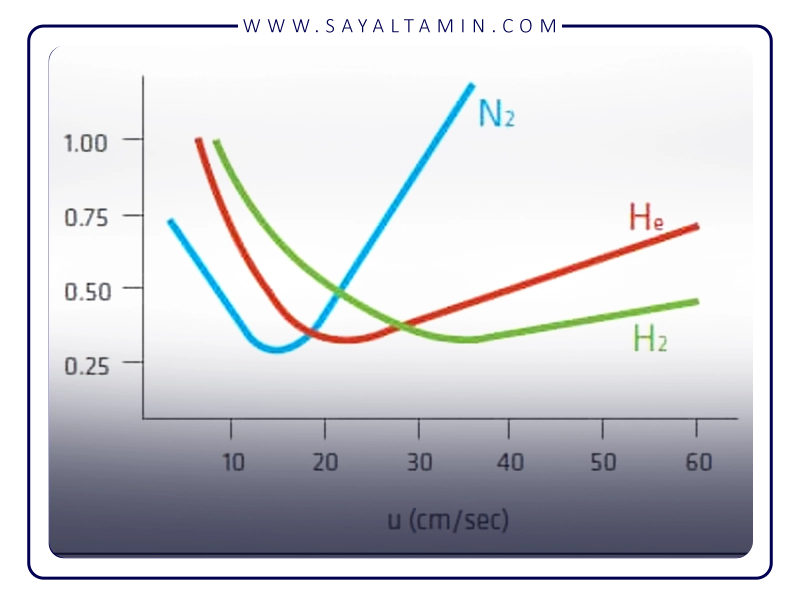
- Helium: Has a high transfer rate and excellent chemical stability, but is more expensive and less available than nitrogen. Also, it can be dangerous if leaked. Helium is often preferred for applications that require high speed and excellent resolution.
- Hydrogen: The fastest carrier gas and can provide the best resolution and shortest analysis time. It also acts as an auxiliary gas in the FID detector. However, hydrogen is highly flammable and explosive and requires the most stringent safety protocols.
Nitrogen gas is recognized as one of the main pillars in gas chromatography due to its combination of safety, economic, and technical characteristics. Although it has limitations in terms of analysis speed and separation compared to hydrogen and helium, it is a very suitable and efficient option for many everyday, educational, and industrial applications. By observing practical tips and optimizing operating conditions, nitrogen can provide high performance in analytical processes and play an important role in improving the accuracy and quality of results.
————————————————–
References


